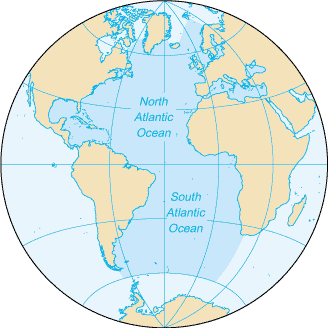
The Atlantic Ocean separates America, in the west from Europe and Africa to the east. It extends from the Artic Ocean, in the north, to the Antarctic in the south. The equator divides it artificially into two parts, North Atlantic and South Atlantic. Its name comes from the Greek Atlas, one of the titans of Greek mythology.
It is S-shaped and extends over 80 million km², and is the second largest ocean, after the Pacific Ocean, covering approximately 20% of the surface of the Earth.
The width of Atlantic varies from 2848 km between Brazil and Liberia to 4830 km between the United States and the north of Africa.
The underwater cordilleras situated between Baffin Island, Greenland and Scotland have become established as the border between the Artic Ocean and the North Atlantic.
To the east, the Straits of Gibraltar forms the border with the Mediterranean Sea; to the east, the arc formed by the Caribbean Island separate them from the Caribbean Sea.
To the west there is an artificial connection between the Atlantic and the Pacific through the Panama Canal.
To the south east, the separation with the Indian Ocean is established by convention, by way of the 20º E meridian. To the southeast the division is established on the deepest line which goes from Cape Horn to the Antarctica peninsula, in the Drake Passage.
It has an average depth of 3,743 m which is obtained thanks to a large plateau of nearly 3,000 m deep which constitutes most of its floor, joined to the large depression which can be found on the edges of the same and which almost reaches 9,000 m. near Puerto Rico. Despite this, the number of islands is relatively few.
The salinity of the Atlantic Ocean is 36 grams of salt per kg of water and the most fished species are the sardine, herring and cod. In addition, it is the most important Ocean on Earth from a commercial point of view.